Perspective on Eliminating Food Waste

DANIELLE TODD, IS THE EXECUTIVE DIRECTOR OF MAKE FOOD NOT WASTE Landfilled food is one of the primary sources of climate change due to two main reasons. First, food decomposing in landfills emits methane, a greenhouse gas 25 times more potent than carbon dioxide. Second, landfilled food represents a waste of land, water, and transportation resources that cannot be reclaimed. Given the substantial volume of food we send to landfills, methane emissions are skyrocketing and our resources are depleting at an alarming rate. Annually, Michiganders discard more than 2 billion pounds of food, resulting in approximately one-third of our landfills being composed of food waste. This excessive waste leads to the negative impacts of extreme weather such as flooding and power outages. It deteriorates air quality, threatens our food supply, and endangers vital plants and animals. Consequently, the State of Michigan, along with the U.S. government and the United Nations, has set a target to halve food waste by 2030. However, with 2 billion pounds of food still being landfilled annually, achieving this goal within six years presents a major challenge. Despite the fact that the problem is so great, eliminating food waste from our landfills is not all that difficult compared to other climate-related changes we need to make. Yes, it’s something we all must do, but it’s also something we all can do. According to the United Nations, more than half of the food waste comes from our homes. That means all of us can make a huge difference in this issue by changing how we handle food in our kitchens. For a fun way to get started, join our 7 Day Food Waste Challenge. You’ll learn the basics and begin to set up some habits that will drive down the amount of food you throw away. Of course, food waste happens outside of homes too. And if we’re going to reach the State’s goal in less than six years, we need a concerted plan. That’s why Make Food Not Waste has launched The 2030 Project, focusing on Southeast Michigan, the region with the highest population density. Concentrating efforts in this area is strategic, given that a larger population corresponds to greater amounts of waste. The project’s objective is to divert all food waste from landfills in the top 15 cities in the region. By collaborating with 17 local and national partners, Make Food Not Waste is crafting a detailed plan incorporating best practices in food waste reduction from across the country. The project’s approach underscores two critical principles: first, there is no singular solution to food waste. Second, we can only stop food waste by working together. While skeptics may argue that completely eliminating food waste from landfills is unattainable, we feel otherwise. It does not require the invention of groundbreaking technology or a defiance of natural laws. Rather, we simply need to stop throwing our food in the garbage. While establishing infrastructure, logistical frameworks, and educational programs pose challenges, they are not insurmountable. The alternative—continuing to waste our resources and make our planet hotter – is not something we can live with. Learn more at www.makefoodnotwaste.org. Be sure to subscribe to our newsletter for regular updates on sustainable business practices in and around Detroit.
The Impacts of the Gordie Howe International Bridge on a Community
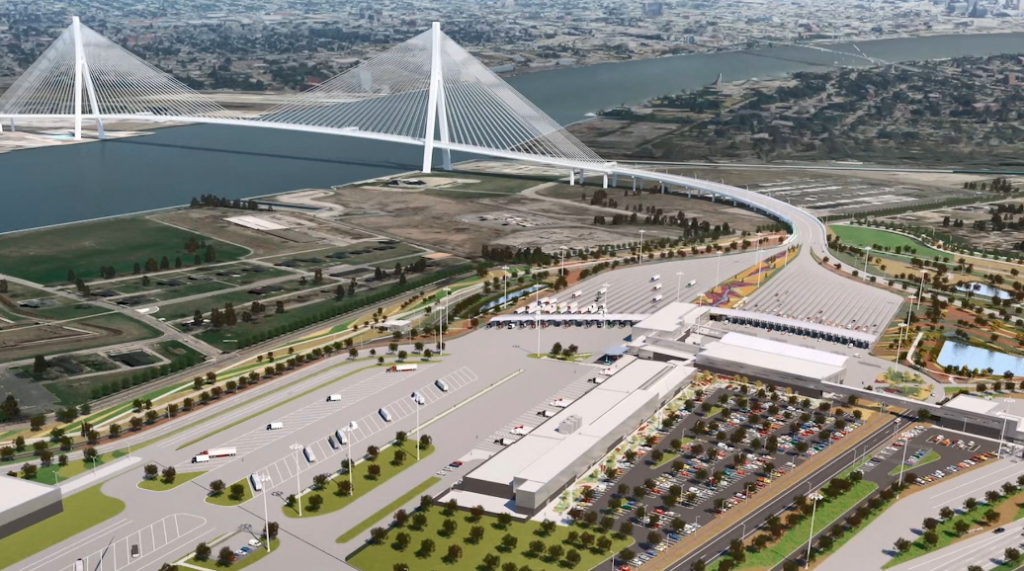

The Gordie Howe International Bridge – currently under construction – is a 167-acre suspension bridge spanning .53 miles, which is the longest main span of any cable-stayed bridge in North America. The impacts of the construction and future operations of the bridge in the Delray area in Southwest Detroit are formidable. Finding ways to assist businesses and residents and keep the community healthy and sustainable while a once-in-a-lifetime infrastructure project like this occurs has been the focus of several community groups. SBN Detroit spoke with Simone Sagovac, project director at the Southwest Detroit Community Benefits Coalition, and Laura Chavez-Wazeerud-Din, president and CEO of the Southwest Detroit Business Association, who are leading initiatives in the community to ensure the interests of businesses and residents are protected. The Southwest Detroit Business Association (SDBA) is a coalition of businesses and community interests committed to facilitating a stable and economically healthy Southwest Detroit. The Southwest Detroit Community Benefits Coalition is a community-initiated organization of residents and stakeholders in the direct impact area of the Gordie Howe International Bridge, whose mission is to seek protection for the quality of life and health of those facing impacts. Q: What impacts are the construction of and existence of the Gordie Howe International Bridge having on the Delray area? Sagovac: It has reshaped the entire neighborhood. One-third of the Delray community has been replaced by this development; 250 families were relocated, and more have chosen to move. Over 50 businesses are gone, and others are trying to figure out how to remain prosperous. Many small businesses are owned by people who live in Southwest Detroit. For the hundreds of residents still living in Delray, community amenities are no longer there, and more truck impacts are coming. Chavez-Wazeerud-Din: The transformation of the Delray community is undeniable, and while we understand that progress often brings change, our focus remains on addressing challenges faced by local businesses. The ongoing street closures pose challenges for customers trying to reach the area, while construction-related dust and debris impede pedestrian traffic. As a result, some businesses have opted to relocate downriver. Q: What is your organization doing to address these issues and mitigate the risks for residents and businesses? Sagovac: We helped initiate a Home Swap program with the city where residents can swap their homes for a land-bank house. About 100 families have chosen to do this. These houses are fully renovated, including new roofs, furnaces, HVAC, interiors, and more. This is a great program, but there are only so many land bank homes available to meet the needs, and some residents want to stay. For those who moved, it’s tough to replace a community you once were a part of. The I-75 Environmental Mitigation Program offered home mitigations such as improved HVAC systems, insulation, and new windows to address noise and air quality impacts from increased truck traffic. The Delray Home Repair Program provided these same options for new roofs and furnaces. We are also working with the state and the University of Michigan on air monitoring and tracking emissions. We’re working with other Southwest Detroit organizations and SDBA on truck traffic solutions – dealing with trucks that are currently being rerouted into neighborhoods and creating significant challenges for residents and the business corridor. Chavez-Wazeerud-Din: The SDBA supports nearly 900 local businesses by offering access to meaningful programs and resources. One resource is our Façade Improvement program, which has been instrumental in helping businesses maintain their relevance and appeal. We’ve extended this program to businesses located on Springwells Street and West Vernor Highway, among other areas. We also are actively engaged with the bridge authority, advocating for a portion of the recent $2.3 million grant funds to be allocated directly to businesses in Southwest Detroit. In addition, we are developing an Experience Southwest Detroit Campaign, recognizing that the increased traffic resulting from the bridge will impact the area. Our goal is to encourage people to stop for meals and retail purchases, allowing them to truly experience the character of Delray and Southwest Detroit, rather than simply passing through. Q: What is being done in terms of buffering and preserving the neighborhoods? Sagovac: We are still seeking additional buffering along I-75 and truck routes and are working with the city and state on this. This is covered in the Delray Neighborhood Framework Plan. Chavez-Wazeerud-Din: We’re collaborating closely with the city and planning department to enhance the safety of the corridor, prioritizing its walkability once more. West Vernor Highway has unfortunately become a main thoroughfare for semi-trucks, posing serious safety concerns for businesses and residents alike. As a result, we’re actively addressing truck routing issues, and we’re optimistic that the Joe Louis Greenway will alleviate some of the traffic on West Vernor Highway. We are involved in the Detroit Intermodal Freight Terminal project to support businesses and the economy in Southwest Detroit by improving freight transportation opportunities. Q: What are the biggest challenges and opportunities? Sagovac: Living with extreme daily truck traffic impacts the community’s health and quality of life deeply. It also damages and devalues property. We are working with the city and many others to bring all forms of solutions, including better truck routing, new infrastructure and zoning, and other policies that will create a quality of life that any family should expect. We also need the support of trucking businesses to ensure their policies and their drivers respect all the traffic safeguards to protect our shared community. Chavez-Wazeerud-Din: Southwest Detroit embodies resilience, characterized by its gritty spirit and the determination of its do-it-yourselfers, a legacy spanning over a century. Business owners and residents (who are often the same) have been impacted and marginalized for a long time. Despite these challenges lies an opportunity: There are funds and resources available to build a more sustainable community. This community, with its rich history and vibrant culture, is not just worth saving – it’s worth nurturing and celebrating for generations to come. Be sure to subscribe to our newsletter for regular updates on sustainable business practices in and around Detroit.
Unlimited Recycling – 25 Years and Still Evolving

In 1999, Maria Marin tapped into her passion for “doing the right thing for Mother Earth” and started Unlimited Recycling Inc. Today, the company offers total recycling and waste management to companies and individuals nationally with the goal of going global. SBN Detroit sat down with Marin to hear about how her recycling services – and clients – have evolved over the years. Q: Tell me about Unlimited Recycling A: Unlimited Recycling is a comprehensive total waste management company offering one-stop-shop services for any type of waste stream. Our services include transportation of any waste or recycling material, equipment rental, including dumpsters of any size, compactors, balers, and any type of container to properly store and transport material. In addition, we offer reporting, training, and education. To date, we’ve handled millions of pounds of waste. Q: What prompted you to start the company in 1999? A: I worked for the Department of Natural Resources, and we received many calls on illegal dumping in waterways and even backyards. When I became pregnant with my first son – who is now the VP of the business – I was told not to eat the fish out of the Great Lakes due to mercury levels. I was so disturbed by that and felt I needed to do something about this problem. I also had the desire to be independent and have my own business. The opportunity presented itself when I lost a job and was looking for next steps. I decided it was time and that I could start my company and shape it any way I liked. The opportunities were limitless, so I named it Unlimited Recycling. We started with universal waste such as fluorescent lamps, batteries, electronic equipment, etc. Eventually, customers started asking about other waste streams, including industrial waste and gradually adding more services. Q: How did your business evolve? A: In 2008, I had the opportunity for an Army contract – they wanted solid waste management for recycling and trash. This would require trucks and dumpsters in an industry I did not know anything about. It took three months for me to learn the business, and the contract was awarded two months later. I purchased my first roll-off truck and 13 dumpsters. Our fleet and equipment have grown tremendously since then. Facilities and companies want one vendor to oversee all their recycling and waste management needs, so we have taken this on by managing these companies’ vendors, contracts, billing, dispatching, and purchasing. We went national about three years ago. Q: How have things changed over the years with the recent government mandates and focus on greenhouse gas emissions and sustainability overall? A: It has been very refreshing to see that the State of Michigan and the governor are on board. Last year, Michigan set new policies to increase the state’s 19% recycling rate to 29% by 2029 and organic waste to 45% material recovery by the year 2050. I believe these goals could be achieved much sooner. To do this, we need to spread awareness within our personal and professional communities. We are working with companies such as Walbridge, managing LEED disposal management for the Gordie Howe International Bridge U.S. Port of Entry, Selfridge Air National Guard Base waste and recycling for the last 22 years, and total waste management for Android Industries, Magna, and many other automotive suppliers. When I started the business, people thought I was crazy. Now I don’t have to sell the why. We have people calling us every day. It’s still a challenge, but every day awareness increases more for the need to recycle. Q: You mentioned you also train companies in recycling. What does that look like? A: Yes. Many people still don’t know how to properly recycle and also find it daunting. I go into businesses and implement their recycling program according to their needs. Often, we start with single-stream recycling for offices and train them on acceptable items and materials, containers needed, etc. Many people do not realize that if you put one waste material that doesn’t belong in a recycling bin, it will contaminate the load. Also, there is a misconception that recycling is expensive. We’ll do a cost analysis for companies and show them that being sustainable is not only the right thing to do, it can also be economical. We’ve saved companies thousands of dollars from diverting cardboard alone. Q: Have the needs of your clients changed a lot through the years? A: Yes. Many started with one service and now we are handling all of it. I’ve seen many companies grow in their efforts over the years. They are becoming more environmentally aware, and their corporate offices are setting higher standards for sustainability, so we get requests all the time from current customers asking if we can recycle new additional waste streams for them or find a solution for a waste stream that isn’t commonly known to be recyclable. I think our services and creative solutions help us retain our customers and find new ones through recommendations regularly. I think that credit goes to our amazing team that responds quickly to customer requests and needs. Q: You offer dumpster rental, universal waste recycling, industrial waste recycling, food waste composting, and LEED waste management. What services do companies and institutions use the most? A: All of the above every day! We are getting more and more requests lately for LEED. (Leadership in Energy and Environmental Design). Q: What does your future look like? A: Our goal is to increase our total waste management services to help companies reach their sustainability and zero-waste landfill goals. We started here in Detroit and are now nationwide; however, it has always been in the plan to go global. I want to go back to my roots, to South and Central America, to teach Latin communities how to recycle, providing them with education and resources. I was recently invited to travel to Africa to assist the country with its plan to implement
A Look at EGLE’s Materials Waste Management Division

The Materials Management Division (MMD) of the Michigan Department of Environment, Great Lakes, and Energy (EGLE) oversees solid and hazardous waste programs, radioactive materials activities, a radon awareness program, recycling, and energy programs. We interviewed the director of the division, Elizabeth Browne, to get some insights. Q: How do you think energy efficiency, recycling, and pollution prevention are interconnected when it comes to fostering sustainability in Southeast Michigan? A: I have always felt you can’t have any without the others, and they are all key to having a sustainable system. Maybe it’s my biologist background. Recycling facilitates energy efficiency since it translates to diverting items from landfills. If you have a good system, you are reusing and recycling materials nearby, you save energy by not transporting material across state lines. When we look at energy efficiency, it works the same way. If we decrease the effort and resources put into heating, cooling, water usage, and transportation systems by becoming more efficient, we have more resources to allocate elsewhere. And isn’t that the very heart and definition of sustainability? Q: How do environmental justice and underrepresented communities factor into these efforts in Southeast Michigan? A: They factor in highly. There are federal funding requirements to help regulate this. The federal Justice 40 program deems that 40% of grant funds be used in underrepresented communities. Even before that, this was a focus for us. If you look at any of our requests for proposals, we pay special attention to projects coming from underrepresented communities – places where the community’s ability to be more sustainable has been stressed. We are always trying to level the playing field. Q: You work with state and federal partners, entrepreneurs, companies, organizations, and communities to reduce Michigan’s reliance on nonrenewable energy. Can you tell us more about this work? A: We work with federal partners in seeking every grant opportunity that we feel we have a nexus with. We work with companies and organizations through the Retired Engineers, Scientists, Technicians, Administrators, Researchers, and Teachers (RESTART) program. This is a group of retired professionals who work with entities to identify where they have energy issues or where renewable energy options may be a benefit. We do energy audits for houses of worship, schools, and municipal buildings. In many cases, these buildings are older and not efficient, so we offer ideas on how to improve efficiency and look at renewable options. This helps them save financial resources that they can then allocate elsewhere. We have received grant money through the Charge Up Michigan Program to install fast chargers in communities. Within this program, the cost of charger installation is divided amongst the location owner, the utility provider, and EGLE. This allows us to install more chargers, and it helps the utilities get closer to their energy efficiency goals and benefits the property owner or business. We have worked with communities to replace diesel- and gas-powered vehicles with electric ones, including Willow Run Airport and the City of Detroit. In Detroit, we replaced diesel-powered garbage trucks with EVs. We work heavily with NextCycle and the Centropolis Accelerator program at Lawrence Technological University. These are both programs to support businesses in their early stages. NextCycle is geared toward recycling activities, and the Centropolis Accelerator focuses on clean technology and the circular economy. Q: What are your biggest challenges in materials management? A: The thing that keeps me up at night is navigating grant programs. There is this huge influx of federal money, but there are a lot of checks and balances, and trying to manage the funding appropriately is a challenge. There is a lot of hurry-up-and-wait involved. We have a phenomenal team, and I don’t want to break their backs as they work to move the money out to recipients. Q: What are your highest priorities? A: Moving as much of the funding to those who need it and doing it in a way that is equitable and fair and hits the highest needs. Sometimes we make decisions that aren’t flashy, but the impact they have on that community is significant. A small community getting a few solar panels to help power their community building so the kids have someplace to go after school is a good example. We try to disburse the money in a way that supports as many communities and people as possible. Q: What does the future look like? A: I think it keeps getting brighter. The Michigan Legislature recently passed an eight-bill package that updates solid waste laws and will ensure we have sufficient landfill capacity. We just held our Virtual Michigan Materials Management Conference and had almost 600 people from 11 states represented. Getting EV chargers out across the state and seeing more and more interest in communities in terms of electrification is good progress. There is so much potential for economic growth in the energy and recycling fields. It’s astronomical. This excites me. Every day, I see people and companies that are looking for support and direction on becoming more sustainable. More and more companies understand the need to be sustainable because the public is demanding it, and it’s also for their own good. I encourage everyone to reach out to us. People interested in any EGLE grant programs can go to Michigan.gov\EGLE and search for “grants and financing.” For more information about all things Materials Management Division, our web pages can be found at Michigan.gov/EGLE/about/organization/materials-management. Be sure to subscribe to our newsletter for regular updates on sustainable business practices in and around Detroit.
Boosting the Economy and Investing in Communities to Create Sustainable Neighborhoods in Southwest Detroit

The Southwest Detroit Business Association has been in existence for almost 70 years with a mission to support the community’s vision for a healthy, vibrant neighborhood. SBN Detroit spoke to the association’s president and CEO, Laura L. Chavez-Wazeerud-Din about the work being done with both businesses and residents to achieve this. Q: What is the impetus behind the Southwest Detroit Business Association? A: In a nutshell, we are here to dismantle barriers and bring resources to business owners and residents in Southwest Detroit. Q: What kinds of barriers? A: Southwest Detroit is a diverse community. Basic things such as navigating the City of Detroit website are difficult because it’s in English only. SDBA works to dismantle barriers by fostering community engagement and promoting economic inclusivity. We aim to create an environment that protects, promotes, and preserves local businesses and the community by addressing challenges such as economic disparities, access to capital, language barriers for a population that is almost 70% Hispanic, and enhancing the overall business ecosystem in Southwest Detroit. We also help residents and business owners navigate the new developments in the area. We are happy to see the city thrive but don’t want that to happen to the detriment of this very historic and culturally relevant community. Q: Your programs include a focus on business development. Tell me about this. A: One way we do this is through our Façade Improvement Program that’s been in existence for twenty years. Some might call this a beautification project, but I think it’s a sustainable model for our businesses. This program helps business and property owners improve their storefronts by providing grants for architectural services and reimbursement for up to 50% of construction costs. The scope of this program has grown through the years and we’ve expanded it to include multiple business corridors in Southwest Detroit, such as W. Vernor Hwy, Michigan Ave, Springwells, Mexicantown, and Junction just to name a few. It has been funded by JP Morgan Chase for the last 17 years and we are now looking for a new funder. We also have a Small Business Advocacy Center. This year we were able to leverage funding from the state of Michigan and bring $800K in equity investments to minority-owned business owners for projects and job creation. An example of this is Dunamis Clean Energy Partners. They were awarded $321K to build out a second line to produce electric charging stations. Another shining star for us this year was saving 16 food vendors that were slated for closing by the city. These vendors failed to receive certifications and pay the associated fines. This was a result of the vendors not understanding the process due to the language and communication barrier. Many didn’t even know they were slated for closing. We worked for months to ensure that not one of them closed, and that was a huge success. Overall, we work to make sure all development and infrastructure is inclusive and equitable to residents and businesses and reflects the culture of the community. An example of this is the La Joya Gardens development. This is an affordable housing mixed-use, mixed-income building that will provide 53 residential units and include retail on the first floor. It is a new building, construction began in 2023. The community named this complex via a naming contest we held. Q: Elaborate on how you work with businesses to facilitate the continuation and enhancement of a stable, economically healthy community. A: We are here to serve everyone from young start-ups to those doing business for decades. We collaborate with partners and other non-profits to bring resources and we are a small business resource hub. Our business community does not always feel safe and comfortable in seeking out resources outside of the community, so we facilitate bringing resources to them here on-site. We are a trusted advisor and conduit with a mission to help our businesses thrive and to make sure that Southwest Detroit is an integral part of the city. Q: Fill us in on your work with the Southwest Detroit Greenlink Project. A: The work we do here is making sure that we are thoughtful and strategic in terms of urbanization and population growth. The ultimate goal is to make Southwest Detroit a tourist destination. We work to get buy-in from the community and preserve the stories of the community. We have run multiple engagement meetings, open houses, surveys etc., to make sure the voice of the community is heard. Two components make up the vision of the Southwest Detroit Greenlink. The first is to complete the Greenlink and all of its sections and the second is to link the Southwest Detroit Greenlink to the other community greenways. Goals of the Greenlink include encouraging residents to walk and bike, giving tourists a welcoming place to frequent local businesses and restaurants, enhancing the economic value of residential and commercial property, and facilitating investment in homes and new businesses. Q: What are your biggest challenges? A: Funding. Also making sure people understand that this work is relevant. The City of Detroit has a lot of layers and it’s our job to secure the resources that are essential and necessary for this community to thrive. Q: What are the biggest opportunities? A: Bridging the digital divide is a big opportunity, and we have had several entrepreneurs rise up since the pandemic to help do so. Engaging with our youth is also a huge opportunity. The Center of Music & Performing Arts Southwest (COMPÁS) is a program that began in 2007 that helps bring mentorship to young people. We work with schools to make sure they understand that SWBDA is a resource. A lot of the kids in the community have been around their family businesses and in many cases these kids are helping to run the websites, and social media, and more. We are a resource to help bring the businesses into the next generation. Q: How can businesses get involved? A: Go to our website to
Daimler Truck’s Detroit Manufacturing Plant – From Diesel to EVs
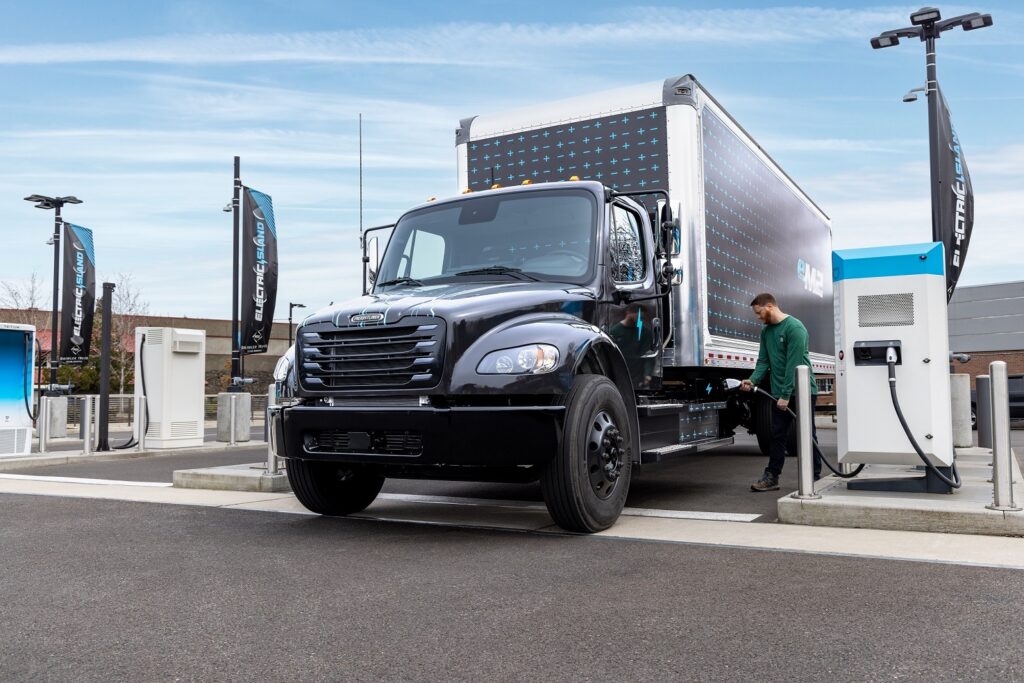

Daimler Truck’s Detroit® Manufacturing Plant produces 400 engines, 250 transmissions, and 1,300 axles daily. The 85-year-old factory is known for making diesel engines but is now working to be a leader in the transition to sustainable transportation. SBN Detroit interviewed Apoorva Mathur, remanufacturing – “reman” – electric product strategy analyst for Daimler Truck North America about the remanufacturing, reuse, and recycling side of the business. Q: How do you approach electrification? A: Our goal is to provide the ePowertrain solution that leads the transition to sustainable transportation. Everything we do pushes toward promoting sustainable transportation. Q: In your role, you focus on the sustainability of Battery Electric Vehicle (BEV) Powertrain components through remanufacturing, reuse, and recycling. How does this work? A: Clearly, part of leading the transition to sustainable transportation is providing an option that has zero emissions, but from an aftermarket perspective, it’s important to be conscious about what we do with components once they come out of the truck. We work to reuse as many components as possible through the remanufacturing process so that we are recycling what we already have. A battery has a lifecycle that extends way beyond what is usable in a vehicle, so to use that battery responsibly it has to have secondary applications. Many times, batteries that come out of a vehicle are used for peak shaving. Peak shaving is utilizing a battery storage system during peak energy usage hours to offset the amount of energy being pulled from the main grid. This reduces the load on the grid. Used batteries can also be used in a microgrid solution whereby some kind of solar or wind-powered system is connected to a battery storage system and energy from solar is used to power the batteries. This is a self-contained situation that does not rely on the grid system at all. Companies can also build used batteries into chargers to provide backup power. So, there are different ways batteries and components can be remanufactured and reused. The recycling component is pretty straightforward. We have a recycling program and a company that disposes of batteries and materials responsibly and also recycles material back into the supply chain. Q: In your role, you also support special projects that advance battery electric vehicle (BEV) adoption, such as creating a charging hub at your Redford location. Can you tell us more about that? A: Yes. The state of Michigan secured $13 million in funding in partnership with Daimler Truck North America and DTE Energy to develop the mobility charging hub earlier this year. We will build a multimodal charging hub there, helping companies to transition their fleets. The charging hub will support heavy trucks and also passenger vehicles and more with the intent to help the entire community transition to EVs. Q: What is driving your change to electrification? A: The largest driver is a combination of emissions standards becoming stricter and also a greater focus on sustainability as a whole on the global stage. Daimler Truck is committed to the Paris Agreement globally, and we are doing our part to provide our customers with zero-emission options. Daimler Truck as a whole is looking for what best suits our customers’ needs, and we are electrifying products across the board and will continue to go down that path. We are also looking at other options such as hydrogen. We need to explore everything to ensure we are giving the best options to our customers. Q: What drives your passion for what you do? A: This is so new for all of us. I’m constantly learning. We are faced with something new every day when comes to requirements from a regulatory perspective and we are constantly getting customer feedback. It’s unchartered territory for all of us and we are all taking this learning journey together in this industry. That’s fun for me. It’s not the business as usual that Detroit Diesel has been doing for 85 years. It’s new and different and exciting. Q: What are the biggest challenges? A: Again, it’s unscripted. It involves so much effort as an industry to make this switch. We can build the product, but we also need the infrastructure. There are gas stations on every corner but supporting EVs is brand new. Also, we need support from utilities. Grid support requires more resiliency as we switch, and there is a lot of work to be done here. When we say we are transforming the transportation industry we mean it. We are taking every component and turning it into something different and it requires so much from everyone. Q: What are the opportunities? A: We’ve seen a whole new level of energy and innovation coming from all sides. New suppliers and players coming into the space every day. It’s exciting to see these companies coming into the industry to push and innovate. On the infrastructure side, it’s the same. New data companies are looking at how to use power in areas to help the grid. There are new charging management systems, new charging suppliers, etc. It’s given the industry a chance to innovate and go outside the norm of what we provide. Q: How do you think the work you are doing impacts Southeast Michigan in terms of innovation? A: Detroit is the place to be when it comes to sustainable transportation. And Detroit is the hub for all things mobility. The Battery Show North America is in Detroit each year, and there is so much knowledge at that show. It’s all being done here. Detroit is the center of competency. It’s a great place to learn and innovate and partner and work within. Q: What does the future look like? A: We will see change on the roads around us. Electric cars are growing in production and adoption in this area. We will see different types of technology being used for different applications as we learn what’s effective. We will see a mixed mobility strategy across the board and that’s exciting. I also
Fishbeck: Working to Keep Natural Resources in Focus
Fishbeck is a 67-year-old consulting firm focused on engineering, environmental sciences, architecture, and construction management with ten offices in Michigan, four in Ohio, and one in Indiana. We spoke to Senior Engineer Lillian Woolley about the company’s internal sustainability practices, as well as their clients. Q: What would you like us to know about Fishbeck? A: Our goal is to provide all-in-one solutions to clients and to do that, we have many technical professionals completing a wide variety of work. Our technical staff has worked on some great projects for clients to support client sustainability initiatives, and I think that many Fishbeck employees enjoy those types of projects the most. Our technical teams like the challenge of pulling off a project that is considered a “win-win,” and we often get the opportunity to do that. One of my favorite projects that we facilitated was the construction of a solar garden on a brownfield site in Cadillac, Michigan. Q: Has Fishbeck always had a focus on sustainability? A: Fishbeck started as a civil engineering firm that worked on water and wastewater treatment system projects more than 67 years ago. Over the years, different disciplines have been added, including environmental engineering, but there has always been a strong focus on helping preserve and enhance the natural resources around us. Fishbeck employees are active in several organizations like the 2030 Districts, U.S. Green Building Council, and more. Q: Do you have an internal sustainability team? A: We have a Sustainability Committee comprising representatives from most departments. Beyond the work we do for our clients, the Sustainability Committee considers firm-specific sustainability issues from an employee’s point of view, as well as from the point of view of the general public. The committee has recently released a survey inside the firm to gauge interest and benchmark sustainability efforts. Using that data, they will present a plan for becoming an even more sustainable organization. Your website says Fishbeck’s core purpose is to help people realize their visions while benefiting society. Can you tell us more about that? A: Most Fishbeck employees want to work on technically challenging projects that leave the world – or their client – in a better place after the project is finished. For example, Fishbeck is working with the Kent County Department of Public Works on its Kent County Sustainable Business Park. Kent County has an ambitious goal to “Reimagine Trash” and to divert 90% or more of its trash from the landfill before 2030. The new sustainable business park will include facilities to recycle solid waste. Our civil engineers designed the site work and utilities, while others designed the stormwater management system. Our environmental team is working on the wetlands permit and other environmental permits. Who wouldn’t love to work on a project so promising? Q: Fishbeck achieved a Wildlife Habitat Council (WHC) Conservation Certification for its office headquarters in Grand Rapids. Tell us about this. A: Fishbeck’s Grand Rapids Office is truly beautiful and includes more than 6 acres of wetlands. There is a large pond and, depending on the time of year, you can see all kinds of birds and other wildlife! To become certified and to document our commitment to being good environmental stewards, Fishbeck ecological professionals surveyed the site, outlined a baseline inventory, and then implemented a plan to enhance the habitat. We recently had a Girl Scout troop come to our office to make bat houses, which we will install at the site. Q: What are examples of your internal sustainability initiatives and goals? A: Not only do our architects work with clients on LEED certification, but the Grand Rapids office buildings and landscape management are certified by the Leadership in Energy and Environmental Design (LEED) rating system. As part of its LEED certification, Fishbeck implements best management practices to benefit adjacent ecosystems. Our Facilities Department unveiled a new recycling program earlier this year, including a compost program. They are also reviewing the downstream impact of our programs and processes. The company has a hybrid work policy so employees can work from home. We are each given 8 hours of volunteer time to use during work hours during the year. Our 17 office buildings have smart systems that turn off lights and lower heat when employees are not in the office. Q: What are some examples of client work that involve sustainability in Southeast Michigan? A: Fishbeck has worked with clients in Southeast Michigan on stormwater management projects, others on boiler or HVAC systems to reduce energy consumption, as well as work on a potential recycling facility. A few years back, we were doing a lot of energy assessments, and we are excited to be doing projects now identified in those assessments. Q: How important is choosing partners and suppliers that also have a sustainability focus? A: Scope 3 greenhouse gas emissions can be much higher than Scope 1 and 2 emissions, so paying attention to partners and suppliers is important. I encourage my clients to have a good understanding of their carbon footprint to ensure that when making changes they are moving in the right direction. It is fairly easy to switch suppliers and double your footprint if you are not careful. Q: What are your biggest challenges when it comes to sustainability? A: Communications. In many cases, the most sustainable approach may be cost-effective, but it takes time and effort to make those projects happen. You need to be knowledgeable about available grants and rebates. You need to understand all options available, and you need to be able to communicate the benefits to all affected stakeholders. We make an effort to ensure we look at every option as well as advise our clients on making the best decision for the environment. Q: What are the biggest opportunities? A: The biggest opportunities are available in performing energy assessments and ensuring your facility is operating at its most efficient. This is because both utilities in Southeast Michigan offer rebates and similar programs allowing
Resiliency Hubs, Waging a War on Trash, and Increasing African American Home Ownership

In 2022, Monique Baker McCormick was re-elected for her third term as Wayne County Commissioner of District 6. She serves Redford Township and Northwest Detroit in the community where she grew up. SBN Detroit spoke to McCormick about the sustainability initiatives she’s been involved in and how they impact residents and businesses in her community. Q: How does sustainability integrate with your position and the work you do as a Wayne County Commissioner? A: I think elected officials must support our communities and in doing so we need to protect the environment and quality of life for today and for future generations. Q: You are involved in so many committees and initiatives, can you give a couple of examples of how sustainability comes into play? A: We recently received a $1.1 million grant to create Wayne County resiliency hubs to reduce our carbon footprint in Wayne County. When I became the chair of Health and Human Services, I became involved with the toxic waste coming from Ohio to Wayne County following a train derailment. This is an environmental issue, a human rights issue, and a civil rights issue, and impacts the quality of life for all of us. As a commissioner, I don’t dig into how cities manage their environmental programs, but I can help on a county level to get funds and to help with programming necessary for the communities. Within the Economic Development Committee, we do have more say in how the operation of sustainability of Wayne County unfolds and how the resiliency hubs work as well. Q: How does this work impact businesses in your district? A: I think the work we do to reduce our carbon footprint and improve the quality of life in Wayne County impacts all of our citizens and businesses and will only help them grow and flourish. I think it helps to drive new businesses to the county as well. Q: You created the Wayne County Commission Youth Council (WCCYC). What is the impetus behind this? A: I had a long journey to becoming a commissioner. I started as a young Democrat and worked for the Democratic party and began to see first-hand how our democracy works and also how it does not. I want the next generation of leaders to understand that if you don’t fight for something, have a voice, or don’t have a seat at the table then don’t expect that someone is going to fight for you. If you want to see change in your community change starts from the bottom up, and that means all of us getting involved in the process. The Wayne County Commission Youth Council helps young people understand this and empowers them to get involved in the process. The goal is to take youth from varied socioeconomic backgrounds and multicultural neighborhoods and help them become socially responsible community members. They pick their topics. We have worked on gun reform, mental health in schools, economic oppression, and more. They do voter registration and outreach, community service, and other issues. We travel to Lansing to meet legislators to make their voices heard regarding what they want to see change in Wayne County. Q: Do you think the youth that are involved now will have an impact on Southeast Michigan businesses as they join the workforce? A: One girl comes to mind – a tenth grader who was an introvert who did not want to speak in meetings at first. She didn’t know she had a voice. She evolved and eventually became the Youth Council President, speaking at all of the meetings and doing interviews, etc. Now she knows she can use her voice for change and for good. Another former member is now the president of his college council on campus. The program also has an internship component. One of our members worked for the mayor’s office in Northville. They go on to do the work that we start. Q: You have led efforts to mitigate foreclosures and increase African-American homeownership. How does this tie to sustainability regarding developing communities and the economy? A: The sustainability of Black and Brown communities starts with the American dream of home ownership. With home ownership you build equity. You buy a home and the value increases over time and once that increases you have this equity. But we’ve seen generations of wealth that have started with home ownership to then be wiped out by freeways. This causes generational economic oppression. It’s difficult to sustain a quality of life when you are always starting behind. Since 2008, African American home ownership is back down to the levels it was in the late ‘60s and early ‘70s all over the country. Detroit has more renters now whereas years ago there were more homeowners. We have to be intentional about how we address this. There are still redlining issues. There is still a lack of ability to get loans. There are a lot of issues around trying to get back to where were. Q: What is the war on trash that you initiated? A: This is an anti-littering campaign. It’s about advocacy that pushes the government and the community to do the right things around trash and littering. When we started the campaign, one of the first issues to address was to ensure our community had trash cans. I worked with the city of Detroit and the Downtown Detroit Partnership to purchase 50 trash cans and enlisted community volunteers to put the cans at city entry points, bus stops, etc. We partnered with elementary schools to try to embed early on that if you live in a community, you should be proud of that community and help to keep it clean. Our messages of “Love Where You Live” and “Don’t Stop and Drop” prompted kids to create art projects around clean communities, maintained trash around their schools, and more. It’s pushing to keep communities clean and green because there is more trash, there is more crime. Q: How do you think
America Recycles Day in Detroit, November 15th

NATALIE JAKUB, IS THE EXECUTIVE DIRECTOR FOR GREEN LIVING SCIENCE, AND A LEADERSHIP COMMITTEE MEMBER FOR SUSTAINABLE BUSINESS NETWORK DETROIT America Recycles Day held annually on November 15th holds immense importance as it serves as a powerful reminder of the critical role recycling plays in conserving resources, reducing waste, and protecting the environment. This annual observance encourages individuals, communities, and businesses to take concrete steps toward sustainability by pledging to recycle and promoting recycling education and initiatives. It reinforces the idea that recycling is not just a one-time effort but a continuous commitment to creating a greener, more sustainable future for generations to come. America Recycles Day inspires collective action and underscores that every small recycling act contributes to a significant positive impact on our planet. ENHANCING RESIDENTS’ ACCESS TO RECYCLING SERVICES For nearly two decades, Detroit has been proactively enhancing residents’ access to recycling services as part of its broader sustainability mission. Acknowledging the importance of diverting recyclable materials from landfills to minimize environmental impact and conserve resources, the city has implemented initiatives such as expanding curbside recycling pickup, improving access to public space recycling, and fostering partnerships with local organizations. These strategic moves aim to make recycling more accessible and convenient for Detroit’s residents, empowering the community to actively participate in sustainable practices and contribute to a cleaner, greener city for all. GREEN LIVING SCIENCE At the forefront of Detroit’s sustainability journey stands Green Living Science (GLS), a nonprofit organization dedicated to educating Detroit residents about waste and recycling. Initially established in response to the Detroit Public Schools Community District’s request for recycling and conservation education, GLS has grown to provide a range of educational programs aimed at instigating behavior change for a more sustainable society. SERVING RESIDENTS GLS serves Detroit’s 600,000+ residents who have been adversely impacted by the trash, air pollution, and debris pervading communities. The city launched a curbside recycling program in 2015 and contracted GLS to teach residents about recycling and sign them up for free recycling carts. GLS remains the recycling and outreach contractor for the Department of Public Works (DPW), educating residents about recycling services available to them and working closely with block clubs and community groups throughout the city. One of GLS’s flagship programs, the Bee Green Business initiative, launched in 2014 in response to the corporate sector’s need for effective recycling and waste reduction solutions. This program educates and certifies companies in Southeast Michigan committed to responsible corporate citizenship. By training businesses to establish waste reduction and recycling systems and educating their staff on correct usage, Bee Green Business supports companies in minimizing their environmental footprint. Moreover, it recognizes and celebrates businesses that are leading sustainability in Michigan. Southeast Michigan, with its historical legacy of manufacturing and innovation, has emerged as a vibrant hub for sustainability initiatives, embracing the principles of responsible business practices. GLS envisions a future for the region where sustainability is integral to business operations, and where companies prioritize environmental impact alongside financial success. To realize this vision, GLS focuses on reducing waste through recycling and composting advocacy, partnering with local businesses to ensure recyclable materials are diverted from landfills, thus reducing the environmental burden. CIRCULAR ECONOMY GLS champions sustainable sourcing practices, encouraging businesses to embrace the circular economy, which minimizes waste and maximizes resource efficiency. These initiatives help bolster the regional economy while diminishing the environmental repercussions of long-distance transportation. While Southeast Michigan has made significant headway in its sustainability journey, it grapples with challenges stemming from its industrial past, including pollution and environmental degradation. Nevertheless, GLS’s emphasis on circular economy principles and waste reduction contributes to overcoming these challenges and forging a cleaner, more sustainable city. Remediation and cleanup efforts continue to address these issues. We are seeing businesses adopting circular economy principles, minimizing waste, and maximizing resource efficiency which will help address and overcome the legacy not dedicated to creating a cleaner city. Green Living Science plays a pivotal role in Southeast Michigan’s path toward sustainability by serving as a catalyst for change. Through engagement with businesses, schools, and communities, GLS offers valuable resources and educational programs that empower individuals and organizations to embrace sustainable practices. In conclusion, Southeast Michigan stands as a burgeoning center for sustainable business practices and environmental responsibility. As Southeast Michigan confronts its sustainability challenges and strives to attain its goals, the role of GLS in educating, inspiring, and facilitating change cannot be overstated. Together, Southeast Michigan and GLS are forging a path toward a greener, more sustainable future, benefiting all who call this region home. Be sure to subscribe to our newsletter for regular updates on sustainable business practices in and around Detroit.
30-Year Architecture Firm Looks Toward Sustainability in Design

Hamilton Anderson Associates (HAA) sits in the heart of what was once Harmonie Park and is now Paradise Valley – and has since the architecture firm’s start in 1994. Its doctrine is to ‘design sustainable communities that inspire change,’ and this encompasses not only architecture, but interior design, landscape architecture, urban design and planning, and development services. The firm was founded by Rainy Hamilton Jr. and Kent Anderson. SBN Detroit spoke to Hamilton about the firm’s sustainability focus and impact on Southeast Michigan. Q: Tell me about HAA as it relates to sustainability A: This is a big topic. Overall, we are always looking to have a positive impact on our clients’ projects and ultimately their bottom line. We always strive to have their best interests in mind and toward that, we need to be cognizant of the design approach, and how we can spend their funds wisely and thoughtfully. We incorporate products and materials that can be recycled or have been recycled, and that are manufactured locally, whenever possible. We think about how we can craft design solutions that take into account the environment and the planet – such as how we can include passive energy generation like wind and solar power. Also, how we manage stormwater is a significant topic with large impervious areas such as roofs and surface parking areas. All of these things are embedded in our thought process for every project. Q: Has HAA always had a focus on sustainability? A: Yes. As trained architects, it has become more commonplace over the last several decades to have this mindset around sustainability. We have been trained to push for well-crafted design solutions that minimize the impact on the environment. We are conscious of utilizing renewable resources such as lumber. Reforesting serves to replenish these natural resources when done properly. At Hamilton Anderson, sustainability is built into our design processes. It is in our DNA to minimize the impact of building on Earth and be sensitive to the environment. Q: Your website says that HAA designs sustainable communities that inspire positive change. Will you elaborate on this? A: In very simplistic terms, let’s think about a typical day. If we can craft our public rights-of-way to be rich and beautiful with adequate lighting and thoughtful landscaping when people move through these areas their spirits are lifted. You feel a very different reaction if you walk through an area with no investment, no landscaping, and no thought or work put into beautifying the space. These types of conditions can negatively impact one’s psyche. Good design is good business. We want to create places of work, rest, and play toward the best possible experience. Q: What are some examples of this? A: We were excited to be part of the design team for Little Caesars Arena. The urban design solution implemented recessed the seating bowl down below grade to reduce the overall height of the facility on the street. Building elements such as retail outlets and other activities were placed around the bowl and the exterior facades were articulated in varying ways to create a wonderful street environment. The result is an active, energized Woodward Avenue with wonderful streetscapes. As we travel the Woodward Corridor, there are many HAA projects that have been completed and have contributed to the growth of Detroit. Projects include the Wayne State Welcome Center, the Addison Hotel, the Strathmore Hotel, Crystal Lofts, Woodward Place, Hamilton at Midtown, Woodward West, Detroit School of Arts, and City Modern. Our work on the Hudson’s Tower with the Bedrock team involves enhancing the downtown area with this major new landmark building and thinking about how it intersects the ground plane and surrounding streetscapes. We rode by the Port Authority Building the other day that we designed on the Detroit River. We suggested a second floor be added to what was originally going to be a one-story structure. Now, there is a gathering event space on top that takes full advantage of the riverfront views. This banquet and meeting space has had a positive impact on the Port Authority’s bottom line and has enhanced the visitor experience. We are thrilled to be working on the expansion of the Music Hall and how to craft this new building next to the historic Music Hall. This addition will enhance the hall and will shine as a beacon welcoming visitors into this vibrant district. Q: How does developing the economy in Southeast Michigan come into play in your work? A: The projects we help bring to fruition and the overall momentum happening in Detroit play a huge role in sustaining and advancing the economy in Southeast Michigan. When I think about the Henry Ford Health right in Midtown, we are proud to be part of the design team. We are influencing how this large development meets the ground plane and embraces the surrounding community. This is critical for the success of this project. The sheer number of jobs this project will create is good for the city and enhances the future of healthcare in Detroit and Southeastern Michigan. All of this will enhance the livability of our city. Over our thirty years of practice, I’ve seen development and construction blips occur in Detroit. Large projects begin and end and there have been development lulls in between. But now we have momentum. We are seeing sustained growth on many fronts. We are seeing new housing and sustained growth occur that is fueling our economy. Q: How important is choosing suppliers and partners that also have a sustainability focus? A: Very important. We work with many different engineering consultants that follow best practices for sustainable design. Many of our contractors are LEED Certified and employ sustainable practices in constructing projects. Q: What are your biggest challenges? A: We are having difficulty finding professionals to grow our practice. We are currently a firm of 40 professionals and are looking to grow but struggling to find the right team members. Also, quality assurance is critical. We practice internal


